Stack
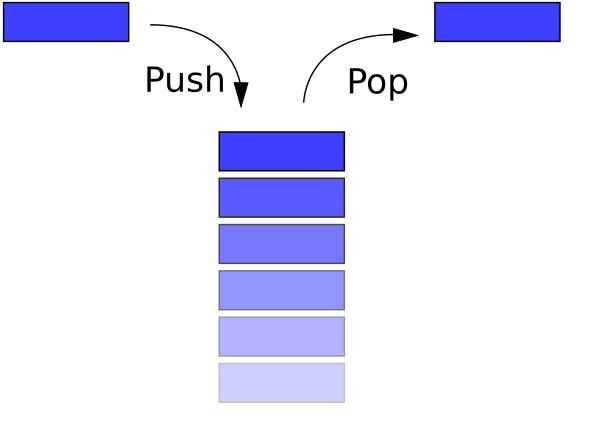
출처: 나무위키
특징
- Stack 자료구조는 LIFO(후입 선출)이라는 특징을 가지고 있다.
- FIFO(선입선출)의 특징을 가지는 큐 형태와 반대이다.
- 구현은 큐에 비해서 쉬운 편이나, 응용할 예시가 매우 많다.
Stack
ArrayStack 사용 예시.
ArrayStack은 스택의 용량을 미리 정해둔다.
솔직히 LinkedStack에 비해서 구현이 매우 쉬웠다. topNode의 정보만 수정/추가/제거 해주면 되기 때문에
maxElementCount를 넘어서는 push는 받지 않고, empty인 경우만 잘 처리해주면 쉽게 구현이 가능했다.
createArrayStack
ArrayStack *createArrayStack(int maxElementCount)
{
ArrayStack *array;
array = calloc(1, sizeof(ArrayStack));
if (NULLCHECK(array))
return (NULL);
array->pElement = calloc(maxElementCount, sizeof(StackNode));
if (NULLCHECK(array->pElement))
return (NULL);
array->maxElementCount = maxElementCount;
return (array);
}deleteArrayStack
void deleteArrayStack(ArrayStack *pStack)
{
StackNode *bottomNode;
int idx = 0;
if (NULLCHECK(pStack))
return ;
bottomNode = pStack->pElement;
while (idx < pStack->maxElementCount)
bottomNode[idx++].data = 0;
free(pStack->pElement);
pStack->pElement = NULL;
free(pStack);
pStack = NULL;
}pushArrayStack
int pushAS(ArrayStack *pStack, StackNode element)
{
StackNode *stack;
int i = 0;
if (NULLCHECK(pStack))
return (ERROR);
if (isArrayStackFull(pStack))
return (ERROR);
stack = pStack->pElement;
stack[pStack->currentElementCount].data = element.data;
pStack->currentElementCount++;
return (TRUE);
}popArrayStack
StackNode *popAS(ArrayStack *pStack)
{
StackNode *popNode;
StackNode *delNode;
if (NULLCHECK(pStack))
return (NULL);
if (isArrayStackEmpty(pStack))
return (NULL);
popNode = calloc(1, sizeof(StackNode));
if (NULLCHECK(popNode))
return (NULL);
delNode = &(pStack->pElement[pStack->currentElementCount - 1]);
popNode->data = delNode->data;
delNode->data = 0;
pStack->currentElementCount--;
return (popNode);
}peekArrayStack
StackNode *peekAS(ArrayStack *pStack)
{
StackNode *topNode;
if (NULLCHECK(pStack))
return (NULL);
topNode = calloc(1, sizeof(StackNode));
if (NULLCHECK(topNode))
return (NULL);
if (isArrayStackEmpty(pStack))
{
printf("STACK IS NOW EMPTY\n");
return (NULL);
}
topNode->data = pStack->pElement[pStack->currentElementCount - 1].data;
return (topNode);
}LinkedStack 사용 예시.
ArrayStack과 크게 다르지 않다. index로 처리하던 부분을 Link로 연결해주는 것.
maxElementCount가 없다는 차이점이 있지만, 결국 스택은 후입선출을 따르기 때문에
topNode만 보면 된다는 것은 다르지 않다.
createLinkedStack
LinkedStack *createLinkedStack()
{
LinkedStack *stack;
stack = calloc(1, sizeof(LinkedStack));
if (NULLCHECK(stack))
return (NULL);
return (stack);
}pushLinkedStack
int pushLS(LinkedStack *pStack, StackNode element)
{
StackNode *newNode;
if (NULLCHECK(pStack))
return (ERROR);
newNode = calloc(1, sizeof(StackNode));
if (NULLCHECK(newNode))
return (ERROR);
newNode->data = element.data;
newNode->pLink = pStack->pTopElement;
pStack->pTopElement = newNode;
pStack->currentElementCount++;
return (TRUE);
}popLinkedStack
StackNode *popLS(LinkedStack* pStack)
{
StackNode *delNode;
if (NULLCHECK(pStack))
return (NULL);
// is empty
if (isLinkedStackEmpty(pStack))
{
printf("STACK IS NOW EMPTY\n");
return (NULL);
}
delNode = pStack->pTopElement;
pStack->pTopElement = delNode->pLink;
pStack->currentElementCount--;
return (delNode);
}peekLinkedStack
StackNode *peekLS(LinkedStack* pStack)
{
if (NULLCHECK(pStack))
return (NULL);
if (isLinkedStackEmpty(pStack))
{
printf("STACK IS NOW EMPTY\n");
return (NULL);
}
return (pStack->pTopElement);
}deleteLinkedStack
void deleteLinkedStack(LinkedStack *pStack)
{
int idx;
StackNode *delNode;
StackNode *nextNode;
if (NULLCHECK(pStack))
return ;
idx = pStack->currentElementCount;
delNode = pStack->pTopElement;
while (idx-- && delNode)
{
nextNode = delNode->pLink;
free(delNode);
delNode = nextNode;
}
free(pStack);
}