HEAP 구조
Heap 구조는 우선순위 큐를 위하여 만들어진 자료구조이다.
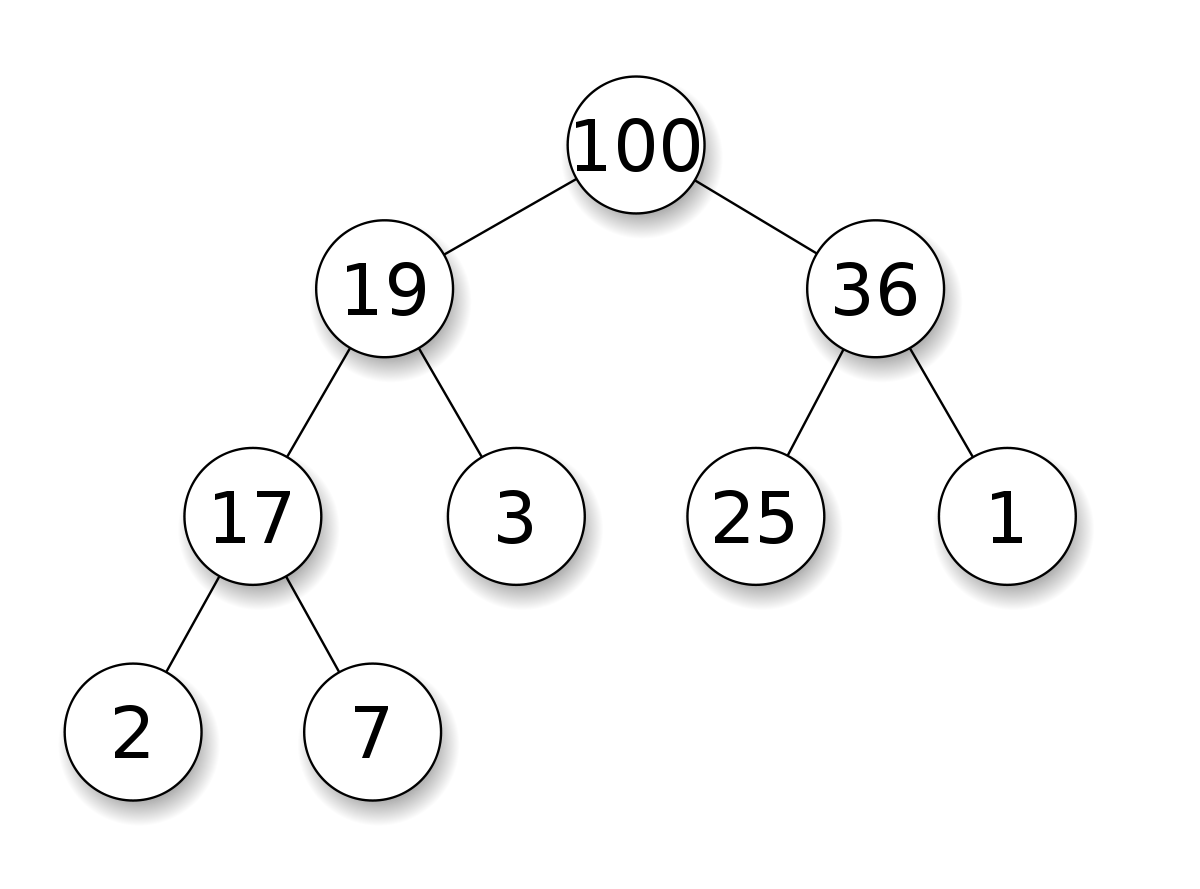
내부적으로 완전 이진트리의 구조를 가지고 있으며, 우선순위 큐를 구현하기 위하여 사용한다.
힙 내부의 데이터들은 모두 우선순위를 가지고 있고, 우선순위가 높은 데이터가 먼저 나간다.
스택은 LIFO, 큐는 FIFO였다면, 우선순위큐는 우선순위에 따라 먼저 나가는 데이터가 결정된다.
힙은 최댓값이나 최솟값을 빠르게 찾는 것에 목적이 있다. (기준에 따라 다를 수 있다.)
힙 트리에서는 중복된 값을 허용하는데, 이 부분이 이진 탐색 트리와의 차이점이다.
HEAP의 구현
힙을 저장하는 표준적인 자료 구조는 배열이다.
DivisionByZero를 방지하기 위하여 첫 번째 인덱스인 0은 사용하지 않는다.
또한 특정 위치의 노드 번호는 새로운 노드가 추가되어도 변하지 않는다.
부모의 인덱스가 i일때, 왼쪽 자식의 인덱스는 i * 2, 오른쪽 자식은 (i * 2) + 1이 되는 형태를 유지한다.
Header
typedef struct HeapArray
{
int currentElementCount;
int maxElementCount;
int *pElement;
HeapType type;
} Heap;Implement
#include "./heap.h"
Heap *createHeap(size_t size, HeapType type)
{
Heap *newHeap = calloc(1, sizeof(Heap));
if (!newHeap)
return (NULL);
newHeap->pElement = calloc(size + 1, sizeof(int));
if (!newHeap->pElement)
{
free(newHeap);
return (NULL);
}
newHeap->maxElementCount = size;
newHeap->type = type;
return (newHeap);
}
// 마지막에 넣어놓고 부모와 비교하면서 올라온다
int insertMaxHeap(int data, Heap *heap)
{
int index;
if (!heap || heap->type != MAX_HEAP)
return (ERR);
if (heap->currentElementCount == heap->maxElementCount)
{
printf("Array is full Now\n");
return (FALSE);
}
index = heap->currentElementCount + 1;
while (index > 1 && heap->pElement[index / 2] < data)
{
heap->pElement[index] = heap->pElement[index / 2];
index /= 2;
}
heap->pElement[index] = data;
heap->currentElementCount++;
return (TRUE);
}
int insertMinHeap(int data, Heap *heap)
{
int index;
if (!heap || heap->type != MAX_HEAP)
return (ERR);
if (heap->currentElementCount == heap->maxElementCount)
{
printf("Array is full Now\n");
return (FALSE);
}
index = heap->currentElementCount + 1;
heap->pElement[index] = data;
while (index > 1 && heap->pElement[index / 2] > data)
{
heap->pElement[index] = heap->pElement[index / 2];
heap->pElement[index / 2] = data;
}
return (TRUE);
}
int deleteMaxHeap(Heap *heap)
{
if (!heap)
return (ERR);
if (!heap->currentElementCount)
{
printf("Array is now Empty\n");
return (FALSE);
}
int result = heap->pElement[1];
int temp = heap->pElement[heap->currentElementCount];
int parent = 1;
int child = 2;
while (child <= heap->currentElementCount)
{
if (child < heap->currentElementCount && \
heap->pElement[child] < heap->pElement[child + 1])
child += 1;
if (temp >= heap->pElement[child])
break ;
heap->pElement[parent] = heap->pElement[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
heap->pElement[parent] = temp;
heap->pElement[heap->currentElementCount] = 0;
heap->currentElementCount--;
return (result);
}
int deleteMinHeap(Heap *heap)
{
if (!heap)
return (ERR);
if (!heap->currentElementCount)
{
printf("Array is now Empty\n");
return (FALSE);
}
int result = heap->pElement[1];
int temp = heap->pElement[heap->currentElementCount];
int parent = 1;
int child = 2;
while (child >= heap->currentElementCount)
{
if (child > heap->currentElementCount && \
heap->pElement[child] < heap->pElement[child + 1])
child += 1;
if (temp <= heap->pElement[child])
break ;
heap->pElement[parent] = heap->pElement[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
heap->pElement[parent] = temp;
heap->pElement[heap->currentElementCount] = 0;
heap->currentElementCount--;
return (result);
}